Masked Edit Control
By defining the Mask property, extensive input validation and formatting is available. The Mask property string is composed of literal characters and of tokens and subtokens defining each input field.
A number of different input fields can be defined using tokens (see the Mask property for a complete list). Literal characters can also be added to the Mask. These characters will be displayed by the Masked Edit control, but the user cannot modify these. Only input fields allow data entry.
Both input fields and literal characters are displayed using the font defined using the Font property. Input fields can be underlined using the PromptUnderline property.
Input fields use the colors defined using the BackColor and ForeColor properties. Literal characters are displayed using the color defined using the BackColor and MaskForeColor properties.
Samples
Visual Feedback
FormattedText - Valid Contents
Samples
Telephone Number

This example allows entry of a telephone number. Area codes cannot start with a "0", only the digits 1 through 9 are acceptable in the first position.
Private Sub Form_Load()
SftMask1.Caption.SizePercent = 0
SftMask1.Mask = "\([M1-9]##\) ###\-####"
End SubSocial Security Number

This example allows entry of a social security number.
Private Sub Form_Load()
SftMask1.Caption.SizePercent = 0
SftMask1.Mask = "###\-##\-####"
End SubDate and Time

One control is used to enter the date and time of an event. A popup calendar is available.
Private Sub Form_Load()
SftMask1.Caption.SizePercent = 0
SftMask1.Mask = "$D $T"
SftMask1.AutoAdvance = True
SftMask1.TabAdvance = True
SftMask1.EditStyle = editSftMaskCalendarDropDown
SftMask1.Contents.DateTime = #7/4/1976 10:00:00 AM#
End SubCurrency


This example shows entry of a currency value with a popup calculator and up/down buttons (spin buttons). This example uses the UpDownPress event so the application has complete control over the starting delay and the progressive increment.
Private Sub Form_Load()
SftMask1.Caption.SizePercent = 0
SftMask1.Alignment = alignSftMaskRight
SftMask1.Mask = "$^C-,8.2"
SftMask1.Label = "|"
SftMask1.LabelPosition = labelPositionSftMaskAuto
SftMask1.EditStyle = editSftMaskUpDown
End Sub
Private Sub SftMask1_UpDownPress(ByVal Up As Boolean, ByVal FieldStart As Long, ByVal FieldEnd As Long, ByVal Counter As Long, Field As String)
Debug.Print "UpDownPress " & Up & " " & FieldStart & " " & FieldEnd & " >" & Field & "<"
If Counter = 0 Or Counter > 5 Then
If Val(Field) = 0 Then
Field = 0
End If
Increment = 0.01
If Counter > 14 Then Increment = 0.1
If Counter > 23 Then Increment = 1
If Counter > 52 Then Increment = 10
If Up Then
Field = Field + Increment
Else
Field = Field - Increment
End If
' If Field > yourMaximum Then Field = yourMaximum
' If Field < -yourMaximum Then Field = -yourMaximum
Field = Format(Field, "###0.00")
End If
End SubPercentage

This example allows entry of a percentage value (0-100) with up/down buttons (spin buttons).
Private Sub Form_Load()
SftMask1.Caption.SizePercent = 0
SftMask1.Alignment = alignSftMaskRight
SftMask1.Mask = "$^3(0,100)"
SftMask1.EditStyle = editSftMaskUpDown
SftMask1.Label = "%"
SftMask1.LabelPosition = labelPositionSftMaskRight
End SubIP Address

This example allows entry of an IP address, consisting of 4 input fields. As the user enters data, the Tab key or "." can be used to move to the next field.
Private Sub Form_Load()
SftMask1.Caption.SizePercent = 0
SftMask1.EditStyle = editSftMaskUpDown
SftMask1.Mask = "$I^03(0,255)\.$I^03(0,255)\.$I^03(0,255)\.$I^03(0,255)"
SftMask1.AutoAdvance = True
SftMask1.TabAdvance = True
End SubVisual Feedback - Valid Contents
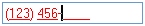

It is possible to provide visual feedback to the user whether the current data entered is valid. In the following example, a telephone number is to be entered. The control's contents are displayed in red until the entire telephone number has been entered. Once the contents are valid, they are displayed using the default window background and foreground colors.
Private Sub Form_Load()
SftMask1.Caption.SizePercent = 0
SftMask1.Mask = "\([M1-9]##\) ###\-####"
SftMask1.Text = ""
End Sub
Private Sub SftMask1_Change()
If SftMask1.Contents.Valid Then
SftMask1.BackColor = vbWindowBackground
SftMask1.ForeColor = vbWindowText
SftMask1.MaskForeColor = vbWindowText
Else
SftMask1.BackColor = vbWhite
SftMask1.ForeColor = vbRed
SftMask1.MaskForeColor = vbRed
End If
End Sub For a more noticeable effect, the background colors could also be modified, or even the Font property.
FormattedText - Valid Contents


The FormattedText property is used to specify the control's displayed text while the control does not have the input focus. This could be used for mandatory fields to highlight that the information has not yet been entered. In the following example, a telephone number is to be entered. As long as the control does not have the input focus and the telephone number has not yet been completely entered, the text "Need phone #" is displayed.
If the mouse cursor moves over the control, the input data is displayed, even if the control does not have the input focus.
Private Sub Form_Load()
SftMask1.Caption.SizePercent = 0
SftMask1.Mask = "\([M1-9]##\) ###\-####"
SftMask1.Text = ""
Call SftMask1_Change
End Sub
Private Sub SftMask1_Change()
If SftMask1.Contents.Valid Then
SftMask1.FormattedText = ""
Else
SftMask1.FormattedText = "Need phone #"
End If
End Sub











